|
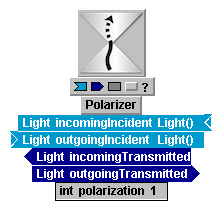
View Inside Polarizer: |
|
Polarizer is an idealized nonphysical model of a polarizing filter. When unpolarized light is incident on Polarizer, the transmitted light is polarized in the sense that it is tagged with a specified polarization state number. If polarized (tagged) light is incident on a Polarizer, and the polarization state of the light matches the state of the filter, then the light passes through unchanged; if the state number of the light is different than that of the filter, the light is blocked.
The unphysical parts of Polarizer properties are that:
(a) Any number of polarization states are allowed, represented by the number 1, 2, 3, etc., with 0 representing "unpolarized" light.
(b) When unpolarized light is put through a Polarizer the intensity is not affected, it is simply tagged with a state number.
The unphysical properties of the Polarizer can actually be rather useful for wave-optics modeling: they provide a simple formal mechanism for separating and combining different beams in a system without inserting a larger number of components that have no effect on the wave properties of the beams.
C++ type |
name |
value |
description |
Parameters |
|||
int |
polarization |
1 |
idealized (nonphysical) polarization state. in effect, each integer except zero specifies a different "polarization" state, and all are taken to be mutually "orthogonal". If set to zero, passes all light unchanged. |
Inputs |
|||
Describes all light incident from the "incoming" direction |
|||
Describes all light incident from the "outgoing" direction |
|||
Outputs |
|||
Describes all light transmitted in the "incoming" direction |
|||
Describes all light transmitted in the "outgoing" direction |
|||