TimeLike provides a robust mechanism for incorporating routines written in Python programming language as simple systems. Such systems are called py-systems.
Example of Python-System
As an example, following is an implementation of system GainPY from BasicMath Component Library:
def GainPY(k, u):
# Usage: (y) = GainPY(k, u)
# Timelike: (double) = GainPY(parameter double, input double)
# Behavior: output-driven
y = k*u
return [y]
Creating Python-System
To create an m-system, use The Available Subsystems Explorer. Right-click on a "Local Systems" node or an a library to which you want to add new py-system to and select New > Python System.
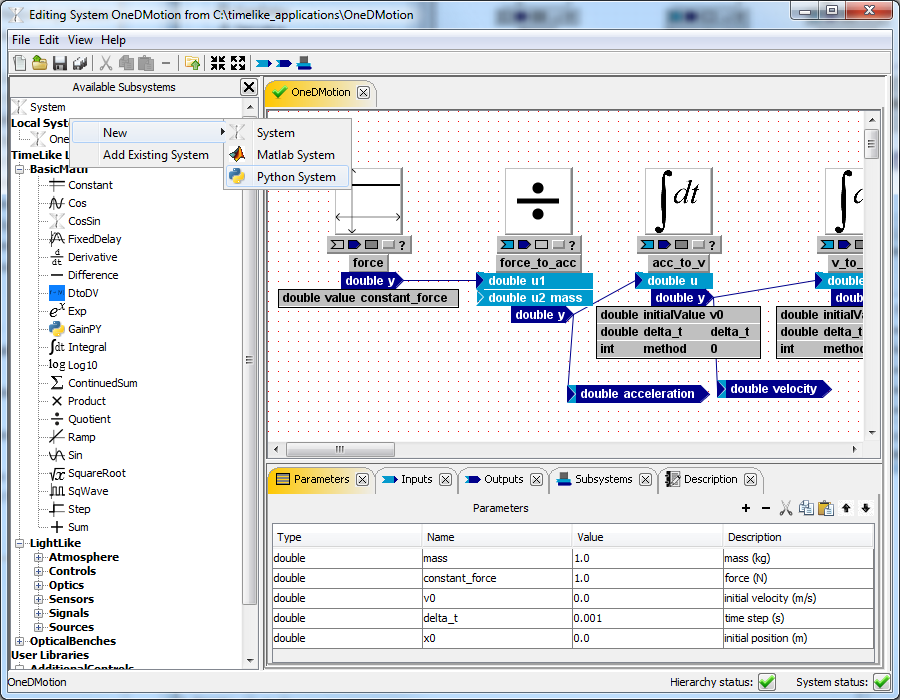
The Python-System Editor window will pop up:
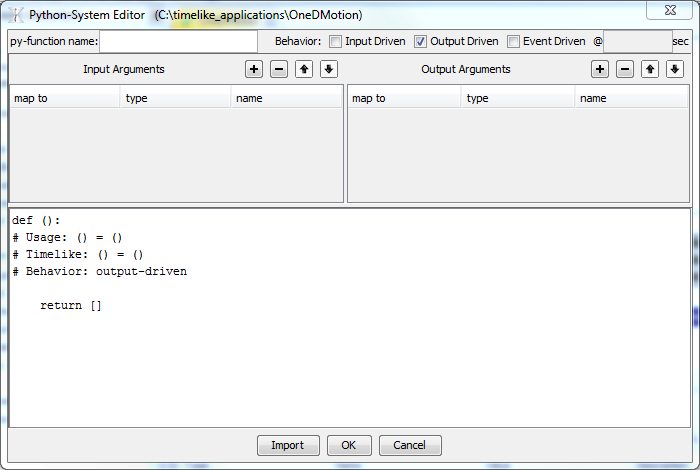
Use this window to enter py-function name, define input arguments, output arguments and behavior (input-driven, output-driven or event-driven) and enter the py-function itself. The first four lines of an m-function are locked because they are automatically generated (and then read in by TimeLike framework) from user-defined inputs,outputs and selected behaviors. See Py-System Editor for the detailed explanation.